Difference between analog and digital computer
Published: 23 Jun 2025
Are you confused about the difference between analog and digital computer? They are both types of computers, but they are completely different from each other. Let’s explore how they are different in function, data, speed, and examples, in very simple words.
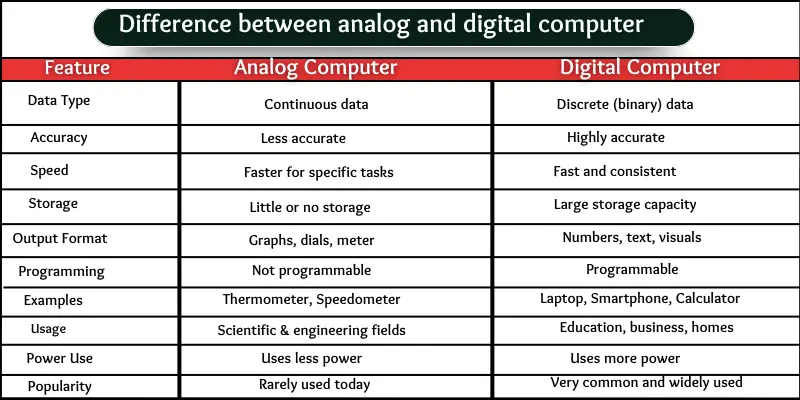
Difference between analog and digital computer
Analog vs digital computers are two different types of computers that work in their unique ways. Let’s look at the key differences between analog and digital computer in a simple list.
10 Differences Between Analog and Digital Computers:
- Type of data they process
- Accuracy
- Speed
- Storage capability
- Output format
- Programming need
- Examples
- Usage area
- Power consumption
- Popularity in today’s world
Type of Data They Process
Analog and digital computers work with different kinds of data. This is the most basic difference between them.
Analog Computer
Analog computers use real-world data. This data is not in numbers but in continuous values. For example, speed, temperature, or sound. These values keep changing and are not exact. Analog computers measure and show this kind of data.
Digital Computer
Digital computers use numbers only. They read data in the form of 0s and 1s, called binary code. The data is clear and exact. Digital computers work step by step and give accurate results.
Accuracy
Analog and digital computers have different levels of accuracy. One gives more exact results than the other.
Analog Computer:
An analog computer is not very accurate. It reads data in a smooth way, like curves or waves. Small changes in input can change the result. So, it may give results that are close, but not exact.
Digital Computer:
A digital computer is very accurate. It works with numbers like 0 and 1. This helps it give clear and exact answers. That’s why most people use digital computers today.
Speed
Speed means how fast a computer works. Analog and digital computers have different speeds because they work in different ways.
Analog Computer:
An analog computer works in real time. It gives answers without any delay. It shows changes slowly and smoothly. But it is not very fast in doing complex tasks.
Digital Computer:
A digital computer works very fast. It solves problems in just seconds. It reads data quickly and gives answers fast. That’s why people use it in homes, schools, and offices.
Storage Capability
Analog and digital computers store data in different ways. Let’s understand how both handle storage.
Analog Computer:
Analog computers do not store much data. They work with real-time signals. These signals keep changing all the time. So, analog computers mostly show results without saving them.
Digital Computer:
Digital computers can store a lot of data. They save numbers, text, pictures, and videos in memory. You can use this data again later. That’s why digital computers are great for long-term use.
Output Format
The output format means how a computer shows the result. Analog and digital computers give results in different ways.
Analog Computer:
An analog computer gives output in physical form. It shows the result using a needle, pointer, or scale. For example, it can move a needle to show speed or temperature. You don’t see numbers on a screen.
Digital Computer:
A digital computer gives output in number form. It shows the result on a screen or monitor. You can see exact numbers, such as 25°C or 60 km/h. It uses digits like 0 to 9 to show clear answers.
Programming need
Some computers need programming to work. Some don’t. This is a big difference between analog and digital computers.
Analog Computer:
Analog computers do not need any programming. They work on their own using real things like speed, temperature, or sound. They don’t use codes or instructions. You cannot change their work by writing a program.
Digital Computer:
Digital computers need programming. You must give them instructions using special languages like Python or C++. They follow these commands to do the job. You can change what they do by changing the program.
Examples
Analog and digital computers are used in different places. They do different types of work in real life.
Analog Computer:
An analog computer works with natural things like speed, temperature, or time. A good example is a speedometer in a car. It shows how fast the car is going. Other examples are a thermometer and an analog clock. These computers show real values in smooth, flowing ways.
Digital Computer:
A digital computer operates with binary numbers, represented by 0 and 1. It gives clear answers in steps. Examples include laptops, mobile phones, and calculators. These computers are very common in homes, schools, and offices.
Usage Area
Analog and digital computers are used in different places. Their working style decides where we can use them.
Analog Computer:
We use analog computers in places where we need to measure real things. These computers are helpful in science labs and hospitals. They check things like temperature, speed, and blood pressure. You can also see them in weather stations and engineering work.
Digital Computer:
We use digital computers almost everywhere today. Schools, offices, homes, and shops all have digital computers. They help us write, calculate, play games, and store information. These computers are fast, easy to use, and very common.
Power Consumption
Analog and digital computers use power in different ways. One needs more electricity, and the other uses less.
Analog Computer:
Analog computers need more power to work. They use electricity all the time while working. These computers have many moving parts. That’s why they use more energy and get warm quickly.
Digital Computer:
Digital computers use less electricity. They work fast and save power. These computers turn parts on and off quickly. That helps them stay cool and use energy wisely.
Popularity in Today’s World
Today, digital computers are used almost everywhere. Analog computers are not very common now.
Analog Computer:
Analog computers were popular many years ago. People used them for scientific and engineering work. But now, we do not use them much. They are mostly found in special places like labs or industries.
Digital Computer:
Digital computers are very popular today. We use them at home, in schools, offices, and hospitals. Laptops, tablets, and smartphones are all digital computers. They are fast, smart, and easy to use.
Conclusion
So guys, it’s time to finish up! In this article, we’ve covered the difference between analog and digital computers in detail. I recommend starting with digital computers first, because they are easier to use and more common today. If you’re just beginning your computer journey, learning about digital systems will help you a lot. Do not forget to check out more beginner-friendly articles on Computer Guide Hub to grow your knowledge!
FAQS about analog vs. digital computer
Here are some important FAQs about analog vs. digital computers:
Digital computers are usually faster than analog computers. They process data quickly and give instant results. That is why we use digital devices in everyday life.
A mobile phone is a digital device. It uses binary code (0 and 1) to send and receive messages, sounds, and pictures. That makes it a type of digital computer.
Examples include speedometers, thermometers, and old-style clocks. These devices show data in a continuous way. They are simple analog machines.
Examples are laptops, tablets, smartphones, and calculators. They work with digital signals and binary numbers. Most modern devices are digital.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks
