Minicomputer
Published: 1 Dec 2024
Have you ever heard of a minicomputer and wondered how it’s different from the computers you use at home or school? While it’s not as big and powerful as the huge mainframe computers, it’s still a special kind of computer that can perform many tasks. It’s like a smaller version of the big computers, and people use them in places like factories or universities.
So, let’s dive in and explore everything you need to know about mini computers!
What are mini computers?
A minicomputer is a type of computer that is smaller than a mainframe but bigger than a personal computer. It can handle multiple tasks and serve several users at once. Mini computers are often used in small businesses or research labs for tasks like data processing. They are more affordable and compact compared to larger computers, making them a popular choice for many industries.
History of mini computer
Minicomputers emerged in the early 1960s as a response to the desire for smaller and more affordable computers. Before that, big computers were very large and expensive. In 1965, companies like Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) introduced the first popular minicomputer, the PDP-8. These computers were smaller than mainframes but still strong enough to do important work. Many companies produced minicomputers, which helped more people use computers more easily. Minicomputers changed the way people worked with technology and made computers more common in offices and schools.
Features of mini computer
Minicomputers have many useful features that make them powerful and helpful for small organizations.
- A minicomputer supports many users at the same time.
- It works faster than personal computers.
- It stores a large amount of data.
- It works as a server in networks.
- It performs many tasks together.
- It is used in small businesses and offices.
- It costs less than mainframe computers.
- It runs multiple programs at once.
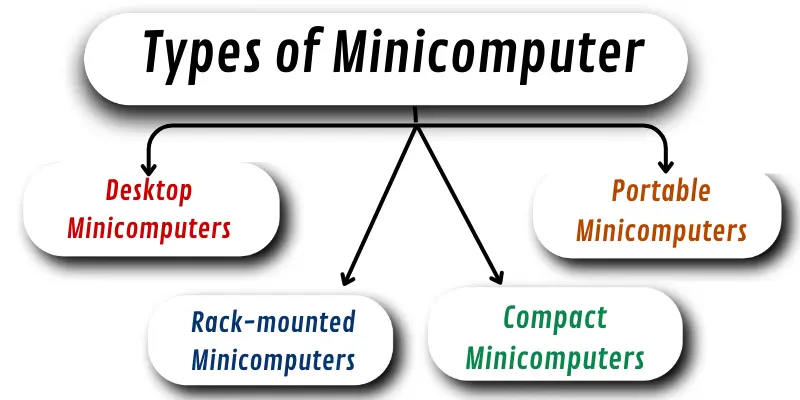
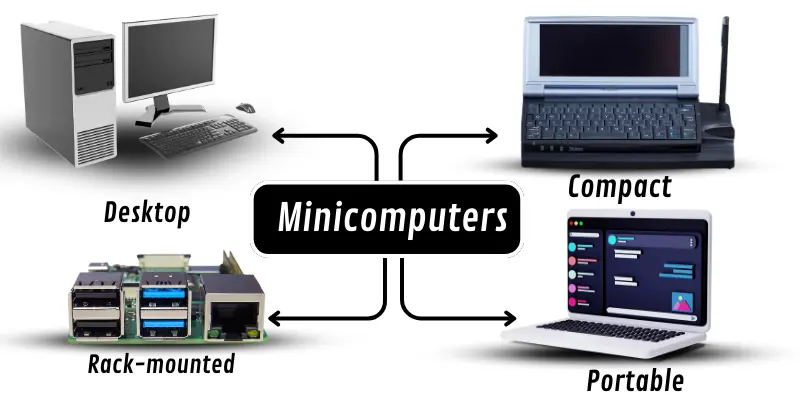
Types of Minicomputer
Here are some types of minicomputers used for different purposes:
- Desktop Minicomputers: Small computers used in businesses that can handle more tasks than personal computers.
- Portable Minicomputers: Small and easy-to-carry computers used for research or specific business tasks.
- Rack-mounted Minicomputers: Minicomputers mounted in racks are often used in data centers for storing large amounts of information.
- Compact Minicomputers: Small computers used for tasks like controlling machines or managing data in factories and labs.
Examples of minicomputer
Minicomputers were smaller than mainframes but powerful enough to handle many tasks. They were used in businesses, factories, and research labs.
Examples:
- PDP-11: A famous minicomputer made by DEC, used for education and industrial work.
- The VAX-11/780 is designed for complex tasks in businesses and universities.
- IBM System/3 is used in small businesses for data processing.
- HP 3000 is popular for managing business operations and databases.
- The Data General Nova is known for its low cost and is commonly used in laboratories and schools.
- Honeywell 200 is used in early commercial and educational systems.
- Tandem NonStop is designed for nonstop processing in banks and airlines.
Characteristics of mini computer
Here are some characteristics of mini computer:
- A minicomputer has a medium size.
- It works reliably without problems.
- It performs powerful tasks easily.
- It adjusts to different types of work.
- It uses less electricity than big computers.
Parts of Minicomputer
The minicomputer consists of the following parts:
- CPU: Processes data and instructions.
- Memory: Stores data for quick access.
- Input Devices: Keyboard, mouse, etc.
- Output Devices: Monitor, printer, etc.
- Storage: Hard drive or SSD for data storage.
- Power Supply: Provides energy to the system.
- Motherboard: Connects all components.
- Bus: Transfers data between parts.
- Cooling System: Prevents overheating.
- Peripheral Devices: Extra devices like printers.
Uses of Minicomputer
Minicomputers are versatile and used in many fields. Here are some of their main uses of minicomputer:
- Business: Manage tasks like payroll and inventory.
- Industry: Control machines and factory processes.
- Data Processing: Handle large data and complex calculations.
- Medical: Control medical devices and patient data.
- Education: Assist in research and administrative work.
- Retail: Manage sales and inventory in stores.
- Communication: Control data in telecommunications.
- Scientific: Support research and experiments.

Advantages and Disadvantages of mini computer
Minicomputers have both advantages and disadvantages. They are useful for many tasks, but they also have some limits. Let’s look at both sides:
| Drawbacks |
|---|
|
Conclusion
So, guys, it’s time to wrap up! In this article, we’ve covered minicomputers in detail. Minicomputers are a great choice for businesses and industries that need reliable and efficient computing without the bulk of larger systems. I recommend looking into how minicomputers can help improve your business operations or personal projects. If you found this article useful, don’t forget to share it with others who might be interested!
Also, don’t miss our detailed guide on the difference between mini and micro computers to understand the key features easily.
FAQs about Minicomputer
Here are some of the most commonly asked questions about minicomputers:
Minicomputers process and store data just like any other computer. They receive input, process it, and then give an output. These computers have central processing units (CPUs), memory, and storage, which help them perform tasks efficiently.
Examples of minicomputers include the PDP series by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) and IBM’s AS/400. These computers were widely used in businesses and factories for tasks like data management and controlling machinery.
Minicomputers are smaller, cheaper, and more energy-efficient than larger systems. They are ideal for businesses that need computing power without the high costs of mainframes. They also require less space and can perform a variety of tasks.
One disadvantage is that minicomputers have less power and capacity compared to larger systems. This limits their ability to handle very large amounts of data. Additionally, they may not be suitable for businesses with complex computing needs.
Minicomputers are often used in businesses, factories, and research labs. They are useful for tasks like managing inventory, controlling machines, or running small databases. They are also found in education and healthcare for specific applications.
Yes, minicomputers are still used today, especially in industries that need compact and cost-effective systems. They may not be as common as personal computers or mainframes, but they serve important roles in many businesses and factories.
Minicomputers are more powerful than personal computers, but they are still smaller and cheaper than mainframes. They are typically used for business and industrial purposes, while personal computers are more common for individual use at home or school.
The price of a minicomputer varies depending on its specifications and capabilities. However, they are generally less expensive than mainframe computers but more expensive than personal computers. You can expect prices to range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
Yes, minicomputers can be upgraded with more memory, better storage, or faster processors like most computers. However, the upgrades may be limited compared to personal computers or more modern systems, so it’s important to check the model’s capabilities before investing in upgrades.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks
