Types of computer network
Published: 12 Oct 2025
From smartphones to massive corporate servers, networks are everywhere around us. These invisible connections make modern life possible. Exploring the types of computer networks gives you insight into how devices communicate, share resources, and keep our digital world running smoothly.
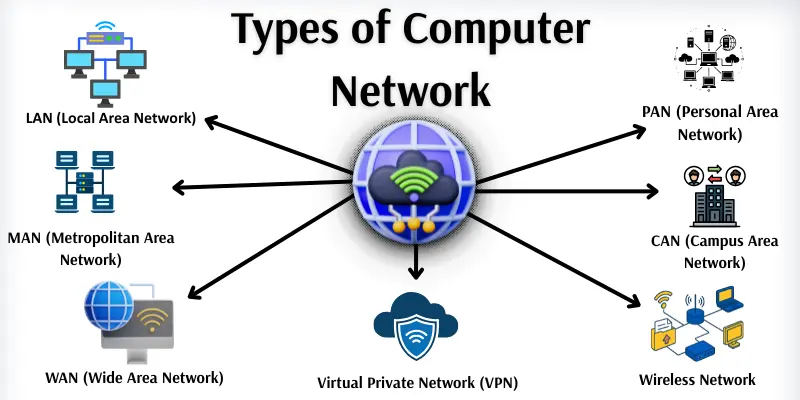
What are the types of computer networks?
A computer network connects different computers or devices so they can share information and resources easily. These networks come in different forms, each created for a particular purpose. Some networks are small and fit for homes or offices, while others can cover entire cities or even countries.
Types of Computer Networks
There are several types of computer networks, each built for a specific environment or need.
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN
- PAN
- CAN
- Wired Network
- Wireless Network
- Client-Server Network
- Peer-to-Peer Network
- Public Network
- Private Network
- Virtual Private Network (VPN)
- Wireless Sensor Network (WSN)
Now, let’s learn different types of computer networks with examples in detail.
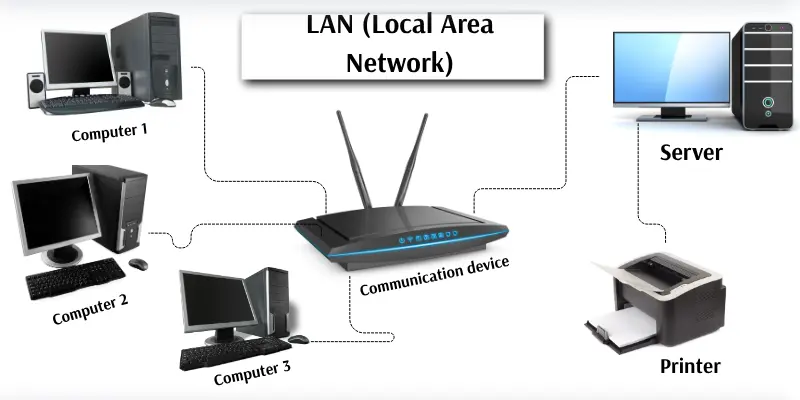
1. LAN (Local Area Network)
It connects computers and devices in a small area. It is usually used in homes, schools, or offices. Devices in a LAN can easily share files, printers, and the internet. It works at a high speed, usually up to 1000 Mbps, because it covers only a small area. LAN uses cables or Wi-Fi to connect devices and is controlled by one main computer called a server.
Example:
In an office building, all employees’ computers are connected to each other and to a central server. They can share files, use the same printer, and access the internet through one network.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
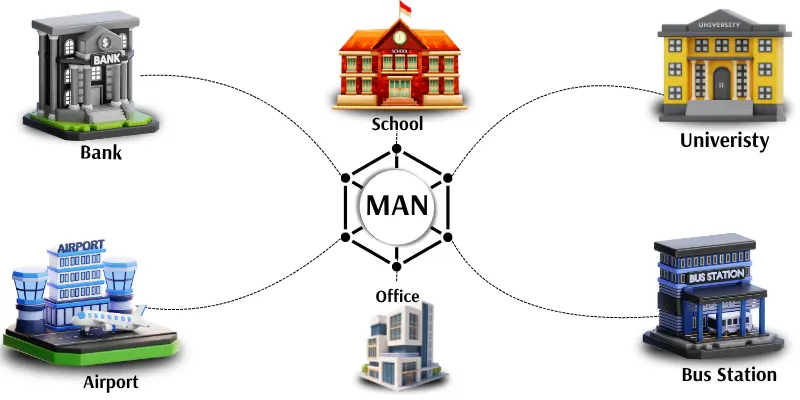
2. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
A MAN connects computers in a big area like a city. It covers more distance than a LAN but less than a WAN. Many offices, schools, and buildings in the same city can be linked using a MAN. This network uses high-speed cables or wireless connections to send data quickly. MAN helps people and organizations share information easily across different locations in the same area.
Example:
All branches of a bank in one city are connected through a Metropolitan Area Network.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
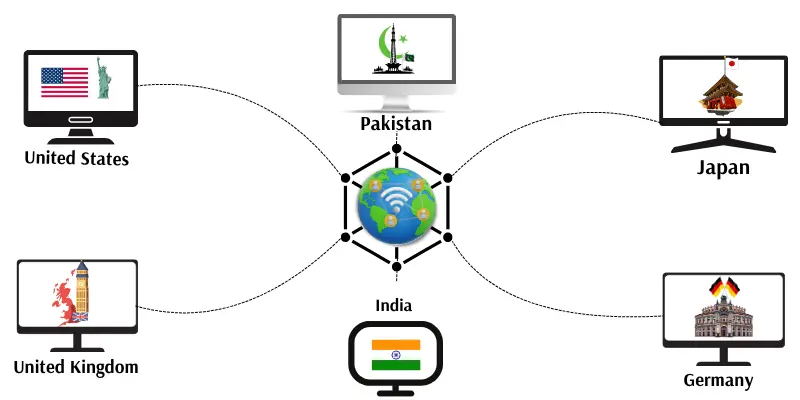
3. WAN (Wide Area Network)
A WAN connects computers and networks in different countries around the world. It is the biggest type of computer network. The Internet is the best example of a WAN. It uses telephone lines, satellites, or fibre cables to send data. WAN helps people and businesses share information from anywhere in the world.
Example:
The internet connects people and computers all over the world.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
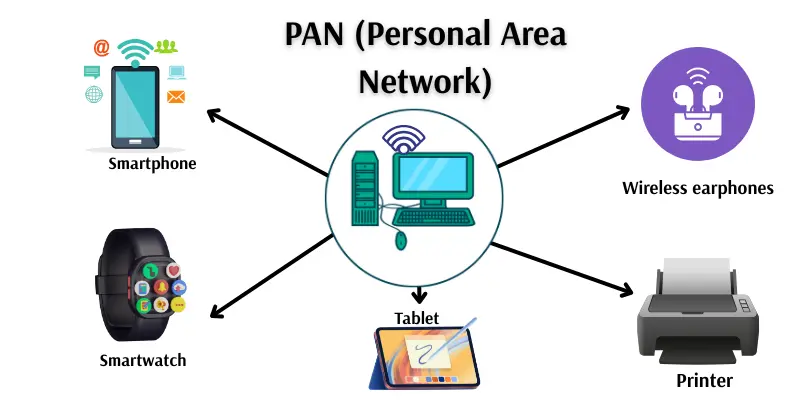
4. PAN (Personal Area Network)
A PAN connects devices that are very close to one person. It covers only a few meters around the user. You can use it to connect your phone, laptop, tablet, or Bluetooth devices. It is the smallest type of computer network. PAN helps one person share data easily between personal devices.
Example:
Connecting a mobile phone to wireless earphones using Bluetooth is a Personal Area Network.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
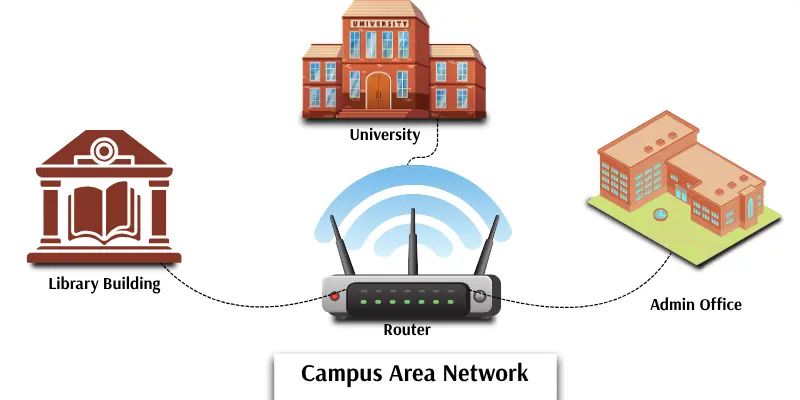
5. CAN (Campus Area Network)
A CAN connects computers and networks within a campus area. It can join buildings in a school, college, or university. This network is bigger than a LAN but smaller than a MAN. CAN helps students, teachers, and staff easily share files, printers, and the internet. It gives fast and reliable communication inside the campus.
Example:
All computers in a university, including labs and offices, are connected through a Campus Area Network.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
6. Wired Network
A wired network connects computers using cables or wires. It is one of the oldest and most common types of networks. In this network, data travels through cables, which makes the connection fast and stable. Wired networks are mostly used in offices, schools, and computer labs. They are safe and give a strong connection without signal loss.
Example:
Computers in a school lab connected with Ethernet cables form a wired network.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
7. Wireless Network
A wireless network connects computers and devices without using cables. It uses radio waves or signals to share data. This network allows people to move freely while staying connected. It is mostly used in homes, schools, offices, and public places. Wireless networks make communication easy and fast without the need for wires.
Example:
Using Wi-Fi at home to connect your phone and laptop to the internet is an example of a wireless network.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
8. Client-Server Network
In this type of network, one powerful computer called the server shares data with smaller computers called clients. The server stores all the data and controls the network. The clients send requests to the server for files, the internet, or other services. This network is mostly used in offices, schools, and companies. It helps manage work and data in one place safely.
Example:
In an office, all employees use their computers (clients) to access files stored on the main computer (server).
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
9. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Network
A Peer-to-Peer network connects computers directly to each other. In this network, every computer acts as both a client and a server. Each computer can share files, data, or printers without needing a main server. It is mostly used in small offices or homes where only a few computers are connected. P2P networks are simple and low-cost to set up.
Example:
Two computers at home sharing files or a printer directly with each other form a Peer-to-Peer network.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
10. Public Network
A public network is open for everyone to use. It is not owned by one person or company. The best example of a public network is the Internet. Anyone can connect and share information on it. But it is less secure because many people use it at the same time.
Real-Life Example:
Using free Wi-Fi in a café or park is an example of a public network.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
11. Private Network
A private network is used by one person, group, or company only. It is protected with passwords and other security tools. This network keeps data safe and private from outsiders. Private networks are mostly used by schools, banks, and offices. They provide fast and secure communication within an organization.
Real-Life Example:
A company’s internal network that only employees can use is a private network.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
12. Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Virtual Private Network helps you use the internet safely and privately. It lets you connect to another network through the internet in a secure way. A VPN hides your real location and keeps your data safe from hackers. Many people and companies use it to protect their online information and stay private.
Real-Life Example:
When someone works from home and connects to their office network using a secure app, they are using a VPN.
| Advantages |
|---|
|
| Disadvantage |
|---|
|
13. Wireless Sensor Network (WSN)
A Wireless Sensor Network, or WSN, is a network made of many small sensors. These sensors collect information like temperature, light, or movement. They send this data to a main computer through wireless signals. WSNs are used in farms, hospitals, and smart cities to check and control different things. This network helps people make smart decisions using real-time data.
Real-Life Example:
Sensors in a smart city that check air quality and send reports to a control center are part of a Wireless Sensor Network.
| Advantages: |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages |
|---|
|
Conclusion
So guys, it’s time to finish up! In this article, we’ve covered types of computer networks in detail. I hope you enjoyed learning how computers connect and share data. I suggest you look around your home or school to see what kind of network is there. If you liked this article, please share it and keep learning more about computers!
FAQs about types of computer networks
Here are a few questions people ask about computer network types.
LAN is used in homes, schools, and offices. It connects computers in a small area. People use it to share files, printers, and internet connections.
A computer network helps people share files, messages, and resources. It saves time and makes communication faster. It is used at home, school, and work.
It helps you understand how devices talk to each other. You learn how data moves safely from one computer to another. Knowing this makes you smarter about technology.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks
