Types of network topologies
Published: 3 Dec 2025
Is your internet slow, or is your office network not working properly? The problem may be in the network’s connection style. Learning about network topologies can help you fix these problems and improve the network. In this guide, we will explain the different types of network topologies in a simple, easy-to-understand way.
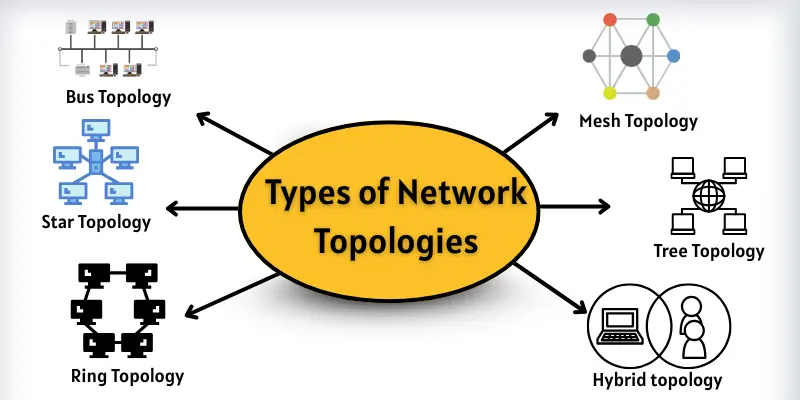
Different types of network topologies
A network topology shows how computers and devices are connected to each other. There are many ways to connect devices, and each way is called a type of network topology. Here are the Types of Network Topologies
- Bus Topology
- Star Topology
- Ring Topology
- Mesh Topology
- Tree Topology
- Hybrid topology
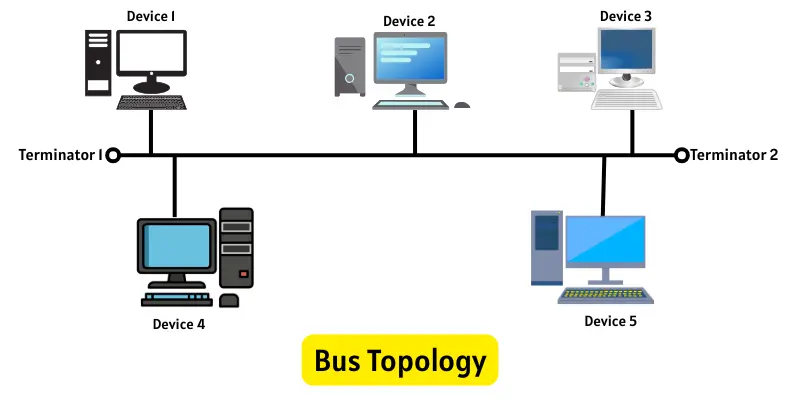
1. Bus Topology
In a bus topology, all computers connect to one long central cable. This main cable works as the communication path for the whole network. When a device sends data, it places the message and the target address on the cable. The signal travels along the cable, and each device checks whether the address belongs to it. The device that matches accepts the data, while all others ignore it. Special terminators at both ends of the cable stop the signal from bouncing back. To avoid data crashes, only one device can send information at a time.
Uses of Bus Topology
Bus topology is simple. It works well in small networks. Here are the main uses:
- People use it in very small networks.
- Schools or offices use it when they want a low-cost setup.
- It works well where only a few computers need to share data.
- Teams use it for quick and temporary networks.
Advantages and disadvantages of bus topology
The bus topology has both advantages and disadvantages. Knowing its advantages and disadvantages helps us understand how it works. Here are the main points:
| Advantages of Bus Topology |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Bus Topology |
|---|
|
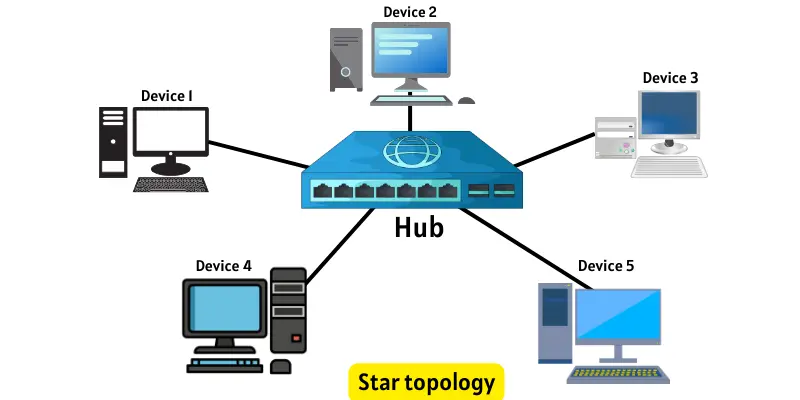
2. Star Topology
In this topology, all computers connect to one central device, such as a hub or switch. This central point handles all data movement. When any device sends information, it first reaches the hub, which then directs it to the intended device. All communication passes through this hub. If one connected device fails, the rest of the network continues to run smoothly. However, if the hub stops working, the entire network is affected.
Uses of Star Topology
Star topology is easy to manage and reliable. It is commonly used in home and office networks. Here are the main uses:
- Schools and offices use it for stable networks.
- It works well when many devices connect to a single point.
- Homes use it for Wi-Fi and wired connections.
- Shops and small businesses use it for easy management.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Star Topology
The star topology has both advantages and disadvantages. Knowing them helps us understand how it works. Here are the main points:
| Advantages of Star Topology |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Star Topology |
|---|
|
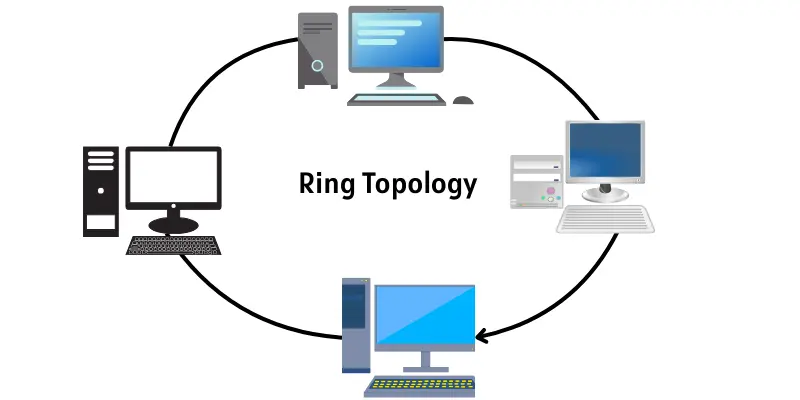
3. Ring Topology
In a ring topology, devices connect in a closed loop, forming a circle. Data moves in one set direction, passing through each device one by one. Every device helps forward the data to the next system in the ring. Because of this chain-like path, one device failure can interrupt the entire network unless special features are used to keep the flow active.
Uses of Ring Topology
Ring topology is used where data needs a set path. Here are the main uses:
- People use it in places where data must move in a clear path.
- It fits well in small or medium-sized offices.
- Companies use it when they want a steady data flow without breaks.
- It helps networks that send data in one direction.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ring Topology
Ring topology has both pros and cons. Knowing them helps us understand their use.
| Advantages of Ring Topology |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Ring Topology |
|---|
|
4. Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, every device has a direct connection to every other device in the network. Data can move on many paths. If one path stops, data uses another path. This makes the network very strong and reliable.
Uses of Mesh Topology
Mesh topology is used where network reliability is very important. Here are the main uses:
- People use it in places that need strong and nonstop connections.
- Large companies use it for safe data transfer.
- It supports networks that cannot afford downtime.
- Smart homes and Wi-Fi systems use it for full coverage
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
Mesh topology has both advantages and drawbacks. Knowing them helps us understand how it works.
| Advantages of Mesh Topology |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Mesh Topology |
|---|
|
5. Tree Topology
It combines star topology and bus topology. Small networks connect like stars to a main bus. It looks like a tree with branches. Data flows from top to bottom and bottom to top. If one device fails, parts of the network may still work.

Uses of Tree Topology
Tree topology is used for large networks. Here are the main uses:
- Schools use it to connect different computer labs.
- Offices use it to link many small groups of computers.
- It helps networks grow step by step.
- It supports large networks with different levels.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tree Topology
Tree topology has both advantages and drawbacks.
| Advantages of Tree Topology |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Tree Topology |
|---|
|
6. Hybrid Topology
In a hybrid, two or more topologies work, such as star, bus, ring, or mesh. This makes the network flexible. Data moves through the parts that work together. If one part fails, the rest of the network may still work.
Uses of Hybrid Topology
A hybrid topology is used when networks need more features and flexibility. It is common in very large systems. Here are the main uses:
- Big companies use it to mix different topologies.
- It works well where departments have different needs.
- People use it when they need both flexibility and strength.
- It supports very large and complex networks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology has both strengths and weaknesses. These points help us understand where it works best.
| Advantages of Hybrid Topology |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology |
|---|
|
Conclusion
That’s it, friends! Let’s wrap it up! In this guide, we explored the different Types of Network Topologies in a very simple way. Always choose the topology that matches your network size, budget, and needs. Start with an easy structure, and upgrade later when your network grows.
If you want to learn more, check out my detailed guide on Computer Networks. It will help you understand networking even better
FAQs about types of topologies
We need different topologies because every network has different needs. Some networks need speed, while others need low cost. Each topology works best in a different situation.
Star and bus topologies work best for small networks. They are easy to set up. They also cost less than other topologies.
The whole network stops working. All data depends on the main cable. This is why bus topology is risky for large networks.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks
