What are Computer Security Threats
Published: 31 Mar 2025
Whenever you use your computer, it’s like opening a door to the internet. But just like you lock your house door to keep out strangers, you need to protect your computer from dangerous things. What are computer security threats? They are harmful things like viruses and hackers that can hurt your computer. To protect your device, you should learn about the different types of computer security. Let’s explore these threats and how to keep your computer safe.

What are computer security threats?
Computer security threats can harm your computer or steal your personal information. These threats can come in many forms, like viruses, malware, or hackers. They may attack your computer by tricking you into clicking on harmful links or by using special software to break into your system. Once they get in, they can damage files or steal private data, like passwords. Knowing about these threats is important so you can protect your computer from harm. Learn more about computer security to keep your devices safe.
Types of Computer Security Threats
Many types of security threats can harm your computer and steal your information. Understanding these threats can help you stay safe online. Here are the top 10 security threats.
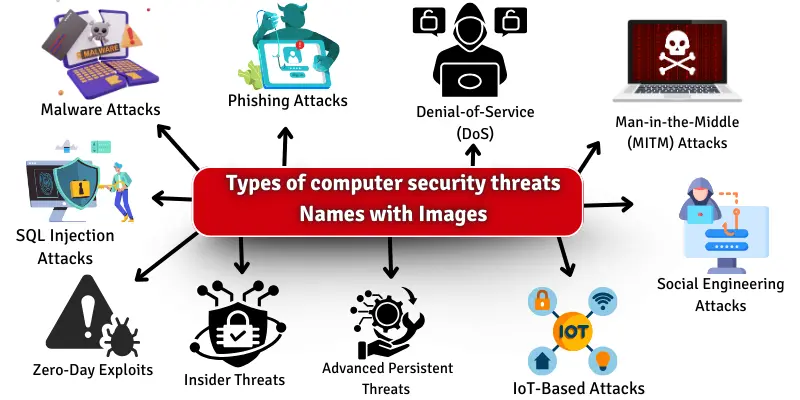
- Malware Attacks
- Phishing Attacks
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) & Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
- SQL Injection Attacks
- Zero-Day Exploits
- Social Engineering Attacks
- Insider Threats
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APT)
- IoT-Based Attacks
Malware Attacks
Malware attacks are harmful software programs designed to damage or disrupt your computer. These programs can enter your system without your knowledge and cause serious issues. Malware can steal your data, damage files, or even control your computer. It’s important to protect your computer from these attacks.
Examples:
- Ransomware: This malware locks your files and demands payment to unlock them
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are tricks used by hackers to steal your personal information. They often look like real emails or messages from trusted companies. The goal is to make you click on harmful links or give away your passwords. Always be careful and don’t trust messages from people you don’t recognize.
Examples:
- Email Phishing: Hackers send fake emails that look like they are from banks to steal your passwords.
- Spear phishing is a more targeted attack in which hackers send emails to specific people, pretending to be someone they know.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) & Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
A denial-of-service (DoS) attack happens when a hacker tries to stop a website or computer from working. They send too many requests at once, which causes the website to crash. A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is similar, but it uses many computers at once to attack. Both attacks make it hard for people to access websites or online services.
Examples:
- Flooding Attack: The attacker sends too many requests to a website, causing it to stop working.
- Botnet Attack: The hacker uses many infected computers to send attacks to a website, overwhelming it and making it crash.
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
A Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack happens when someone secretly listens to your conversation or takes control of the information you send. The hacker secretly places themselves between you and the person you’re talking to. This can happen when you send sensitive information like passwords or credit card details. The hacker can steal or change your information without you knowing.
Examples:
- Wi-Fi Eavesdropping: The hacker uses public Wi-Fi to listen to your online conversations and steal your data.
- Session Hijacking occurs when a hacker takes over your online session and pretends to be you while logged in.
SQL Injection Attacks
SQL injection is a type of attack in which hackers use bad code to trick a website’s database. This allows them to access or change information without permission, and the hacker can steal important data like passwords or credit card numbers. It is one of the most common attacks on websites.
Examples:
- Login Page Attack
A hacker might enter special characters on the login page to access secret information. - Search Bar Attack
A hacker can use the search bar on a website to steal data from the database.
Zero-Day Exploits
A zero-day exploit is a computer attack that happens when hackers find a weakness in software or systems that no one knows about. This means the company or developers haven’t fixed the problem because they aren’t aware of it. Hackers use this gap to attack before anyone can protect against it. It’s called “zero-day” because the attack happens on the first day the vulnerability is found.
Examples:
- Stuxnet Virus: It attacked computers controlling nuclear plants by exploiting a weakness no one knew about.
- Heartbleed Bug: Hackers used this bug to steal information from websites with encryption problems that no one knew existed.
Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks deceive people into sharing their personal information. These attacks do not target your computer or software directly. Instead, they use manipulation and deceit to get you to reveal important details like passwords or bank account numbers. These attacks often seem harmless but can cause a lot of damage.
Examples:
- Pretexting: A hacker pretends to be someone you trust to steal information.
- Baiting: A hacker offers something valuable, like free software, to trick you into downloading harmful files.
Insider Threats
Insider threats happen when people within an organization, like employees or trusted users, cause harm to the system. They can misuse their access to steal information or damage the system. These threats are dangerous because the person causing the harm already has permission to use the system. It’s important to monitor all users to prevent insider threats.
Examples:
- Employee stealing company information
The employee copies or shares private data. - Trusted user spreading a virus
The user clicks on a harmful link, infecting the system.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APT)
Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) are long-term, secret attacks on computer systems. Skilled hackers usually carry out and stay hidden in a system for months or even years. APTs are often used to steal important information without being noticed. They are very hard to detect because they are carefully planned and executed.
Examples of APTs:
- Stuxnet Attack:
This attack targeted Iran’s nuclear plants and damaged their equipment. - Target Data Breach:
Hackers used APTs to steal the personal details of millions of people from the Target store’s computers.
IoT-Based Attacks
IoT stands for the Internet of Things. It refers to everyday devices that connect to the Internet, like smart thermostats, cameras, and refrigerators. While these devices are helpful, they can also be targets for hackers. IoT-based attacks happen when hackers try to control or steal information from these devices.
Examples:
- Smart Home Hacks: Hackers can break into smart home devices like cameras and change their settings without the owner’s knowledge.
- Connected Car Attacks: Hackers can take control of connected cars and mess with things like the brakes or GPS.
Impact of Computer Security Threats
Computer security threats can seriously affect your system, data, and personal information. Understanding their impact helps you take the necessary steps to protect your devices. Here are the key impacts of computer security threats:
- Data Loss: Important files and data can be lost or stolen.
- Privacy Breach: Personal information like passwords can be taken.
- Financial Loss: Cyberattacks can steal money or cause fraud.
- Reputation Damage: Security issues can harm your reputation, especially for businesses.
- System Downtime: Attacks can make websites or systems unavailable.
- Identity Theft: Hackers can steal your identity for illegal actions.
- Malware Infections: Harmful software can damage your computer.
- Legal Consequences: Companies might face legal problems for not securing data.
- Loss of Trust: People may lose trust in a business after a security breach.
- Operational Disruption: Attacks can cause business operations to stop.
How to Prevent Computer Threats
It is very important to keep your computer safe from threats. You can protect your computer in many ways from dangers like viruses and hackers. By following simple steps, you can ensure your computer stays safe and your information is protected. Here are 10 ways to protect your computer.
- Install antivirus software.
- Keep your software up-to-date.
- Use strong passwords.
- Be careful with emails and links.
- Avoid downloading unknown files.
- Use a firewall.
- Back up your data regularly.
- Use encryption for sensitive data.
- Turn off your computer when it is not in use.
- Educate yourself about online security.
Conclusion
So, guys, it’s time to wrap up! In this article, we’ve covered what computer security threats are in detail. To stay safe, install antivirus software, use strong passwords, and avoid clicking on suspicious links. Taking simple steps today can save you from big problems in the future. Protect yourself from these threats and share this knowledge with your friends to help them stay safe!
Common Questions about Computer Security Threats
Here are some of the FAQs about Computer Security Threats
Yes, IoT (Internet of Things) devices, like smart cameras and thermostats, can be hacked. Since they are connected to the internet, hackers can try to control them or steal personal information. Protect your IoT devices with strong passwords and regular software updates.
Antivirus software can protect you from many common threats like viruses and malware, but it can’t catch everything. It’s important to keep your software updated, use strong passwords, and stay cautious online to protect against other types of attacks like phishing.
To protect your children from online security threats, set up parental controls, teach them about safe internet practices, and monitor their online activities. Make sure they understand the dangers of clicking on unknown links or sharing personal information.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks
