What is CPU? A Complete Guide
Published: 22 Sep 2025
Did you know the first CPU was invented by Intel in 1971, and today billions of devices run because of it? The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is often called the brain of the computer because it handles all the instructions that enable your system to function. Without a CPU, no computer, laptop, or even smartphone could function.
What is CPU?
The CPU is an important part of a computer that carries out instructions. It is known as the brain of the computer because it manages and directs most of the important tasks.. The CPU takes input, processes it, and gives output within seconds. It works with memory and other hardware to make sure programs run smoothly. Without a CPU, a computer cannot work at all.
Full Form of CPU
The abbreviation CPU means Central Processing Unit.
- Central means it is the main part of the computer that controls everything.
- Processing means it handles and processes all the instructions given to the computer.
- Unit means it is a single and complete component that performs its job inside the system.
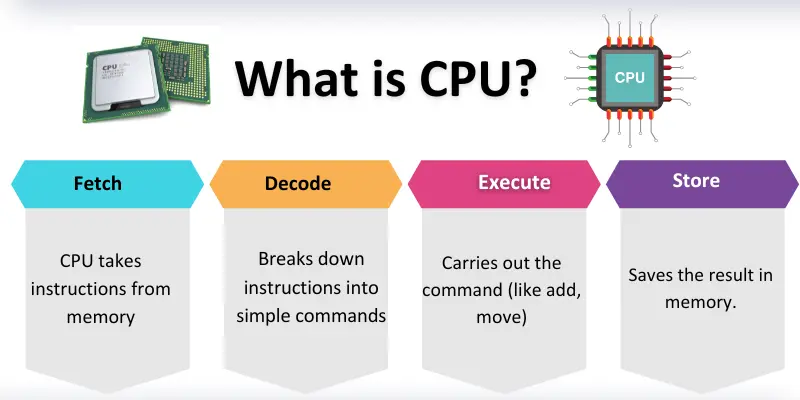
How Does CPU Work?
The CPU works like the brain of the computer. It takes instructions, understands them, and then tells the computer what to do. Every action you perform, like opening a file, typing a word, or playing a game, goes through the CPU. It works step by step and makes sure data moves smoothly between input, memory, and output.
To understand better, let’s look at the process in detail:
- Fetch: The CPU collects instructions from the system’s memory.
- Decode: It changes those instructions into easy-to-follow steps.
- Execute: The CPU performs the action, such as solving math or moving information.
- Store: The output is kept in memory so it can be used later when required.
In short, the CPU follows this cycle—Fetch, Decode, Execute, and Store—millions of times every second to keep your computer running.
Parts of the CPU
The CPU is made of smaller units that work together to process data. Each part has a special role in making the computer function.
- Control Unit (CU): Manages and guides the movement of instructions and data.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Handles math calculations and logic-based decisions.
- Registers: Tiny memory spaces that keep data for a short time.
- Cache Memory: Ultra-fast memory used for quick access to data and instructions.
- Buses: Channels that move data between different computer components.
Types of CPU
CPUs come in different types based on their speed, design, and use. Each type is made to handle specific tasks and performance levels. Here are some types of CPU:
- Single-Core CPU: Processes just one instruction at a time.
- Dual-Core CPU: Handles two instructions together.
- Quad-Core CPU: Handles multiple tasks more smoothly.
- Hexa-Core CPU: Features six cores for enhanced multitasking.
- Octa-Core CPU: Has eight cores for faster performance.
- Deca-Core CPU: Offers ten cores for high-end processing.
- Intel CPUs: Popular processors known for strong performance.
- AMD CPUs: Known for good speed and value.
- ARM CPUs: Used in smartphones and tablets for efficiency.
- Apple M-Series CPUs: Designed for MacBooks and iPads with powerful performance.
Functions of CPU
The CPU performs different tasks to make the computer work smoothly. Here are its main functions:
- Accepts Input: Takes data from input devices like keyboard or mouse.
- Processes Data: Performs calculations and follows instructions.
- Produces Output: Sends the result to output devices like a monitor or a printer.
- Stores Information: Keeps data in memory for quick use.
- Controls Other Parts: Manages and coordinates all hardware components.
Real-Life Example:
When you type a word in Microsoft Word, the CPU accepts the keystroke, processes it, and shows the letter on the screen. At the same time, it controls memory and storage to save your file.
Examples of CPU
Different companies make CPUs for computers, laptops, and mobile devices. Here are some popular examples:
- Intel Core i3, i5, i7, i9: Widely used in laptops and desktops.
- AMD Ryzen Series (Ryzen 3, 5, 7, 9): Known for strong performance and multitasking.
- Apple M1 and M2 Chips: Used in MacBooks and iPads for high speed and efficiency.
- Qualcomm Snapdragon Series: Found in many Android smartphones.
- MediaTek Processors: Common in budget-friendly mobile devices.
- Intel Xeon: Designed for servers and workstations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CPU
The CPU is the most important part of a computer because it controls all tasks. Like everything, it has both strengths and limitations. Let’s look at its advantages and disadvantages.
| Advantages of CPU |
|---|
|
| Disadvantages of CPU |
|---|
|
Conclusion
So guys, it’s time to finish up! In this article, we’ve covered what is CPU? in detail. From its definition to types, functions, and examples, now you know why it’s called the brain of the computer. My recommendation is to always choose a CPU that matches your needs—basic tasks don’t need high-end processors, but gaming and editing do. If you found this guide helpful, don’t forget to explore my other computer articles and keep learning more!
FAQs about CPU
Common Questions and Answers on CPU:
The CPU is the brain of the computer. It takes instructions, processes them, and gives results. Without it, a computer cannot work
Yes, CPU and processor mean the same thing. Both terms are used to describe the main chip that processes instructions. People often use the term “processor” in place of “CPU.”
Examples include Intel Core i3, i5, and i7 processors, as well as AMD Ryzen processors and Apple M1/M2 chips. These are used in laptops, desktops, and smartphones. Each type is designed for different needs.
It is called the brain because it controls all the main functions. Just like our brain tells the body what to do, the CPU tells the computer what to do. Every task is processed by the CPU first.
The CPU helps us with tasks such as typing documents, browsing the internet, playing games, and running apps. Every click and action you do on a computer is processed by the CPU. Without it, nothing would work.
A mid-range CPU, such as the Intel Core i5 or AMD Ryzen 5, is excellent for most beginners. They balance speed, multitasking, and price. You don’t need a very high-end CPU unless you do heavy gaming or editing
The first CPU was invented by Intel in 1971. It was called the Intel 4004. Since then, CPUs have become faster, smaller, and more powerful.
No, a computer cannot work without a CPU. It is the main unit that processes and manages everything. Without it, the system cannot run at all.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks
